The discipline of prompt engineering proves essential when users need to work with artificial intelligence systems, including the large language models (LLMs) ChatGPT, Claude, and Google Bard. Users achieve accurate, relevant, context-driven outputs from AI through the creation of specific, well-organized prompt inputs. The successful execution of prompt optimization requires intensive knowledge about AI behavior responses to prompts and well-honed techniques for obtaining optimal outputs.
This article demonstrates twelve vital prompt engineering techniques that enable users to maximize the capabilities of AI tools while working on content generation and problem resolution operations.
 AI generative tools generate superior results based on the quality which users provide as prompts. Definitions which are unclear within prompts will yield both incorrect and irrelevant outcomes from AI systems although well-designed prompts enable streamlined communication between users and produce superior outcomes. Professional prompt engineering represents the essential method for accessing the maximum performance of AI systems when creating content or implementing code analysis or data investigation tasks.
AI generative tools generate superior results based on the quality which users provide as prompts. Definitions which are unclear within prompts will yield both incorrect and irrelevant outcomes from AI systems although well-designed prompts enable streamlined communication between users and produce superior outcomes. Professional prompt engineering represents the essential method for accessing the maximum performance of AI systems when creating content or implementing code analysis or data investigation tasks.
This set of twelve best practices provides concrete methods to produce productive prompts which enhance AI system performance regarding accuracy and relevance and operational speed.
Write your prompt only after establishing the specific task the AI will execute. Your prompt performance directly correlates to your goals because clearly defined objectives help guide the input text toward meeting your expectations.
A recommended step involves recording the specific goal before building a prompt to minimize meaning confusion.
Computer models achieve superior results by receiving adequate information about the background scope. Providing context allows the model to develop its point of view while making sure the responses match what you need.
For example:
Ambiguity leads to poor results. Your instructions need to be clear to the model, so make each requirement explicit. For instance:
The quantity of information in your prompt determines how accurately the model will answer your request. Short prompts do not provide enough detail, yet very long prompts lead the model to become confused.
Only include the vital information points that will help the AI perform its task effectively. Terminals help you find suitable prompt lengths by trying various options until the best solution appears.
Break complicated multi-step requests and complex questions into separate chunks for better results. The AI process begins by analyzing single components, after which it creates a unified final output.
The request to summarize the report should come first, followed by a suggestion for improvement.
Your selected words during prompt construction determine both the response tone and its level of accuracy. You must choose action-directed verbs such as generating, providing, or analyzing so your expectations become clear to the system.
Make sure to omit slang and metaphors because they may create confusion for the model.
Open-ended promotional items enable participants to express their ideas in innovative ways. For example:
The addition of representative samples to your input directs AI models toward meeting your preferred writing format, together with style requirements. For instance:
The response detail level should be defined through a specified length constraint. For example:
Multiple contradictory requests create confusion in AI systems, which subsequently leads them to generate poor output results. Make sure your instructions contain clear language without any opposing or unclear statements.
Please normalize verbalization when writing because briefness and complete information delivery should not exist in the same instruction. The instruction must specify whether briefness takes priority above completeness in the writing.
The correct use of punctuation systematizes complicated requests so that AI processing systems can accurately interpret the information. For example:
An iterative process called prompt engineering requires repeated tests during development cycles until you reach peak performance levels. You should evaluate the AI system output to modify your prompts according to the evaluation results.
 Create your first draft from the main goal statement.
Create your first draft from the main goal statement.
Successful prompts should be documented for use as reusable templates.
Following these best practices will enable users to achieve the following benefits.
Users who work as developers and occasional tool experimenters using generative AI can boost their LLM interactions through the mastery of these techniques.
The practice of prompt engineering presents two main challenges to users alongside its known advantages.
Challenges can be managed through the combined use of specific and loose directions and effective workflows.
Users achieve optimum performance from ChatGPT and Claude 3 through the art and scientific practice called prompt engineering. The combination of twelve established best practices enables users to generate precise, relevant, creative responses that match their specifications through processes of providing context alongside iterative prompt refinement. Knowledge of prompt engineering will remain essential for users who want to effectively use generative artificial intelligence across healthcare, education, and e-commerce applications. Practicing these techniques provides new and experienced AI users with an ideal foundation for developing their ability to design productive AI inquiries.

Master how to use DALL-E 3 API for image generation with this detailed guide. Learn how to set up, prompt, and integrate OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 into your creative projects

Discover how Replit Agent simplifies coding, testing, and deployment using natural language in an all-in-one platform.

Learn how CrewAI’s multi-agent AI system automates writing full-length articles directly from YouTube video content.
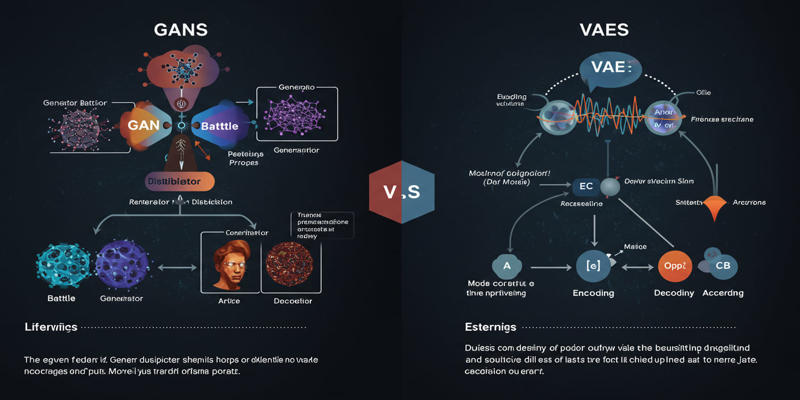
Study the key distinctions that exist between GANs and VAEs, which represent two main generative AI models.

Explore how Meta AI on WhatsApp is revolutionizing mobile use with smart chats, planning, creativity, and translation.

How to set upstream branch in Git to connect your local and remote branches. Simplify your push and pull commands with a clear, step-by-step guide

AI in drug discovery is transforming medical research by speeding up drug development, reducing costs, and enabling personalized treatments for patients worldwide
Master the Alation Agentic Platform with the API Agent SDK capabilities, knowing the advantages and projected impact.

How search algorithms in AI—like BFS, DFS, and A*—solve real-world problems with smart, structured logic. Simple, practical, and human-written insights

Want to run AI without the cloud? Learn how to run LLM models locally with Ollama—an easy, fast, and private solution for deploying language models directly on your machine
JFrog launches JFrog ML through the combination of Hugging Face and Nvidia, creating a revolutionary MLOps platform for unifying AI development with DevSecOps practices to secure and scale machine learning delivery.

YouTube channels to learn SQL, The Net Ninja, The SQL Guy