We’ve hit a point in technology where simply describing an image in plain language can create it instantly. That’s exactly what DALL-E 3, developed by OpenAI, does—it turns text into stunning, detailed visuals. While many use it on websites, developers are now integrating the DALL-E 3 API directly into apps, platforms, and creative tools.
This shift allows for automated image generation tailored to user input. If you’re curious about how to use DALL-E 3 API for image generation, this article lays it out clearly. We’ll cover setup, prompt structure, usage, and real-world applications—all in a simple, no-nonsense way.
To get started with the DALL-E 3 API, you’ll need access to OpenAI’s API services. First, sign up at OpenAI's official platform and generate your API key from the dashboard. This key is critical—it acts like your personal passport to access the DALL-E 3 API and other services provided by OpenAI. Without it, your requests to the API won’t go through. Think of it like a key that only unlocks your specific creative session.
Once your API key is secured, it's time to install the tools needed to interact with the API. Most people use Python for this because it's simple and well supported. A quick setup with pip install openai gives you everything you need to start. From there, you import the openai library and authenticate using your API key, something like:
import openai
openai.api_key = "your-api-key"
That’s the basic structure. From here on, you’re ready to send prompts and receive image responses. But knowing the setup isn’t enough—you need to understand how prompts are crafted and handled, which is where it starts to get interesting.
The most crucial part of using the DALL-E 3 API for image generation isn’t the code. It’s the language. What you say—and how you say it—changes what you get back. Prompts like “a medieval castle under a moonlit sky with glowing blue dragons flying around it” give the AI enough context to build a scene with mood, setting, and visual drama. The richer the description, the better the result.

Using the openai.Image.create() method, you can send these prompts and receive high-quality images in return. The structure is simple:
response = openai.Image.create(
model="dall-e-3",
prompt="a futuristic cityscape with flying cars and neon lights",
n=1,
size="1024x1024"
)
The model field confirms you're using DALL-E 3. The prompt is your visual description. The n field determines how many images you want. Size specifies image resolution. Once this is done, the API responds with a URL where the image can be viewed or downloaded.
Here’s the cool part—DALL-E 3 doesn’t just paint pretty pictures. It understands nuance. You can ask for style-specific visuals like “in the style of 1950s advertising” or “as a watercolor painting,” and it reflects that in the output. The trick is trial and observation. Try variations, play with tone, and you’ll learn how different wording tweaks the results. The DALL-E 3 API isn’t just functional—it’s flexible.
You're not using the DALL-E 3 API just to admire test images in a Python shell. The real value comes when you integrate it into actual tools and workflows. For instance, imagine building a content automation platform that converts blog headlines into social media posts with custom visuals. With a text-to-image prompt generated from the article, DALL-E 3 can instantly produce a matching image ready for sharing—no manual design required.
In e-commerce, this becomes even more powerful. Let users describe their ideal product—like a jacket with specific colors and patterns—and generate a visual representation on the fly. It enhances personalization and reduces dependency on large product photo inventories.
In education, DALL-E 3 can illustrate historical events or story settings. A teacher could type "a bustling Roman marketplace during Caesar's rule" and instantly receive an engaging visual. Similarly, game developers can create dynamic in-game art based on user input or procedural storytelling.
These use cases often combine backend scripting (Python, Node.js, etc.) with a front-end system that fetches and displays the image. Once the prompt is crafted and the API is called, the resulting image URL can be embedded anywhere, seamlessly enhancing digital experiences.
The DALL-E 3 API offers impressive capabilities, but it’s important to recognize its boundaries. One major limitation is usage quotas. Your access depends on the pricing tier you've chosen through OpenAI. Once the quota is exhausted, requests may be delayed, throttled, or rejected until your limit resets or you upgrade your plan.

Errors also come into play. Not all issues arise from syntax mistakes—sometimes prompts are too vague or trigger OpenAI’s safety filters due to sensitive or restricted language. The system is designed this way to ensure responsible image generation, not just accuracy.
Ethics matter, too. Generating content that resembles real people, celebrities, or brands can lead to serious legal issues. Developers must build safeguards that block or sanitize prompts that might cause harm, impersonation, or misinformation.
Context is another subtle constraint. DALL-E 3 responds literally. If your input lacks clarity, the resulting image may be confusing or off-target. It can’t guess your intent—it only mirrors your words.
To navigate these challenges, test prompts across various cases, keep track of results and prepare fallbacks for failed generations. Think of DALL-E 3 as a creative assistant—not a flawless magic wand.
The DALL-E 3 API opens a new door for developers and creators to turn words into visuals with minimal effort and maximum creativity. It's not just about generating images—it's about building smarter, more dynamic experiences that respond to user input in real-time. Whether you're enhancing apps, automating content, or adding visual flair to data, the DALL-E 3 API makes it possible. With the right prompts and thoughtful integration, your ideas can take visual form in seconds.

How search algorithms in AI—like BFS, DFS, and A*—solve real-world problems with smart, structured logic. Simple, practical, and human-written insights

Discover these 7 AI powered grammar checkers that can help you avoid unnecessary mistakes in your writing.

How AI APIs from Google Cloud AI, IBM Watson, and OpenAI are helping businesses build smart applications, automate tasks, and improve customer experiences
How heuristics and optimization in AI power intelligent systems, blending speed with accuracy to improve AI decision-making and real-world problem-solving

Explore the most popular AI programming languages used in artificial intelligence projects. Learn why Python, R, and Julia are leading choices for developers worldwide
Discover the most used Power BI charts to enhance your reports. Learn how each chart improves data visualization and insight.
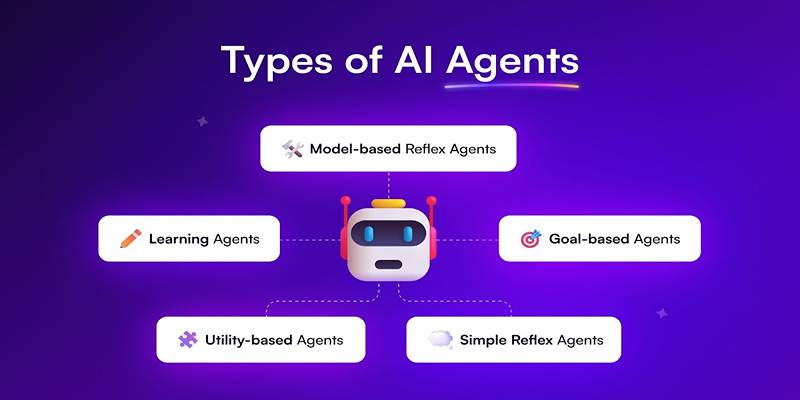
Learn about the main types of AI agents in 2025 and how they enable smart, autonomous decision-making systems.

How to set upstream branch in Git to connect your local and remote branches. Simplify your push and pull commands with a clear, step-by-step guide

YouTube channels to learn SQL, The Net Ninja, The SQL Guy

Learn to excel at prompt engineering through 12 valuable practises and proven tips

How AI’s environmental impact is shaping our world. Learn about the carbon footprint of AI systems, the role of data centers, and how to move toward sustainable AI practices

Drive more traffic with ChatGPT's backend keyword strategies by uncovering long-tail opportunities, enhancing content structure, and boosting search intent alignment for sustainable organic growth